About Medical Nutrition
Medical nutrition encompasses specialised products for nutritional therapy: Oral Nutritional Supplements, Enteral Tube Feeding, and Parenteral Nutrition
Medical nutrition encompasses specialised products for nutritional therapy: Oral Nutritional Supplements, Enteral Tube Feeding (via the gastrointestinal tract), and Parenteral Nutrition (intravenous feeding).
Medical Nutrition helps patients of all ages to address nutritional insufficiencies arising from a disease, disorder or condition, when they are unable to meet their requirements via normal foods.
Medical Nutrition products are to be used under medical supervision. Depending on the situation medical nutrition may be required for short or long term or even for life and may be administered in diverse healthcare settings or at home.
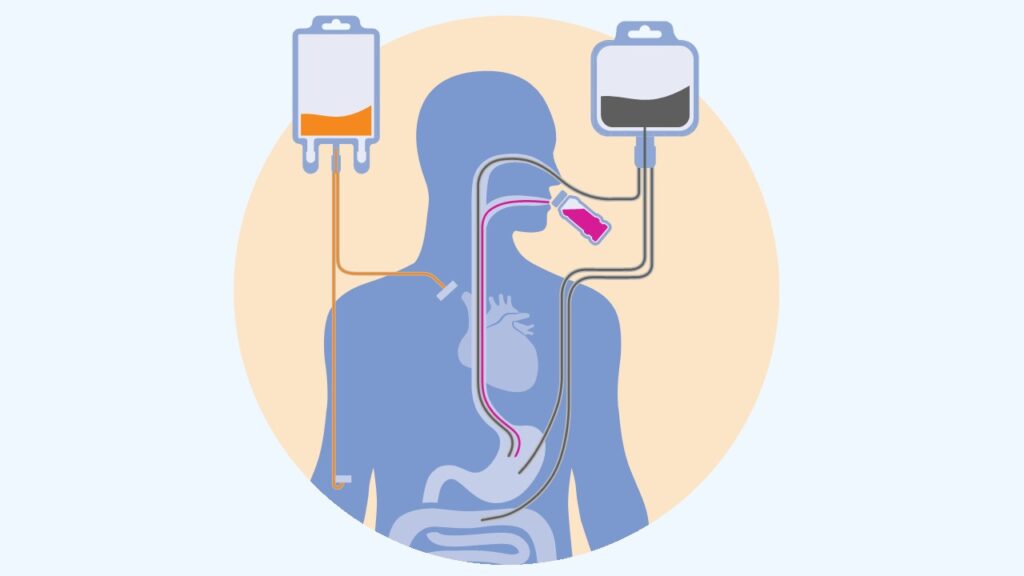
Types of medical nutrition
Oral Nutritional Supplements
Oral Nutritional Supplements (ONS) provide macronutrients and micronutrients and are designed to be consumed orally, thus taste and format are important considerations. ONS are available as ready-to-drink liquids or powders that can be prepared as drinks (also called ‘sip feeds’) but are also available in pre-thickened form.
Enteral Tube Feeding
Enteral Tube Feeding is administered into the gastrointestinal tract via a nasogastric, nasoenteric or percutaneous tube. Enteral Tube Feeding is required when a patient is unable to consume sufficient nutrition via the oral route. Examples include severe cystic fibrosis, cerebral palsy, after a stroke or major surgery, such as head and neck surgery, and critical illness.
Enteral Tube Feeding can be supplementary to oral intake or parenteral nutrition, or can be the sole source of nutrition.
Parenteral Nutrition
Parenteral Nutrition – also known as ‘intravenous feeding‘ – is a method of getting nutrition directly into the blood circulation, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract. Parenteral Nutrition is delivered via a catheter inserted into a peripheral or central vein. Parenteral Nutrition is needed when a patient is unable to obtain sufficient nutrition through normal food, ONS or tube feeding. For instance indications for Parenteral Nutrition include gastrointestinal failure which can occur after surgery or in critically ill patients, short bowel syndrome, intestinal obstruction, a fistula in the gastrointestinal tract, cancer patients with severe mucositis or premature infants.
News
Institution documents
- Commission Notice on the Classification of FSMP (November 2017)
- Regulation (EU) 609/2013 on food intended for infants and young children, food for special medical purposes, and total diet replacement for weight control
- Regulation (EU) 2016/128 as regards the specific compositional and information requirements for food for special medical purposes
- EU Guidance for FSMPs – COM notice on the classification of FSMP (2017/C 401/01)
- CODEX standards on FSMPs – CODEX STAN 180-1991







